The Evolution and Impact of Predictive Analytics in Big Data Applications
Predictive analytics (PA) has become a cornerstone in the world of big data, enabling organizations to make informed decisions by analyzing past observations. As businesses increasingly rely on data-driven strategies, the role of predictive models in sectors like marketing, banking, and healthcare is growing exponentially. Professor Jacob Zahavi from Tel Aviv University has played a pivotal role in advancing this field, particularly through his research on logistic regression-based models. His work not only highlights the importance of accurate prediction but also provides a roadmap for developing robust and reliable PA systems.
Understanding Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics involves using historical data to predict future outcomes. This process typically includes two main stages: building a model that fits the dataset and using that model to predict responses for new data. The goal is to forecast events that lie beyond the original input range. In big data applications, this process becomes more complex due to the high dimensionality and volume of data involved.
Explanatory vs. Predictive Models
Professor Zahavi distinguishes between explanatory and predictive models. Explanatory models are used to understand phenomena based on past data, focusing on causal or statistical relationships. These models aim to find the best fit for the data according to predefined criteria. On the other hand, predictive models are proactive tools designed to predict unforeseen events. They focus on associative relationships between variables and aim to minimize prediction errors.
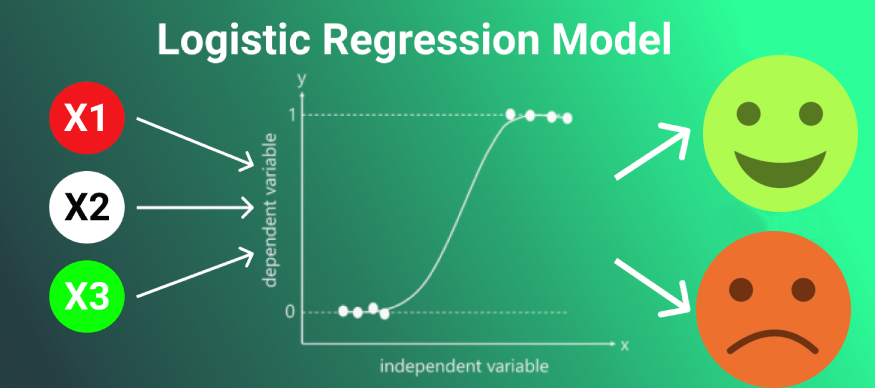
The Role of Logistic Regression
Logistic regression is one of the most widely used techniques in predictive analytics, especially for binary classification problems. It is used to predict the probability of an event occurring, such as whether a customer will respond to a marketing offer. The dependent variable in logistic regression is binary (0/1), representing “no” and “yes” outcomes respectively.
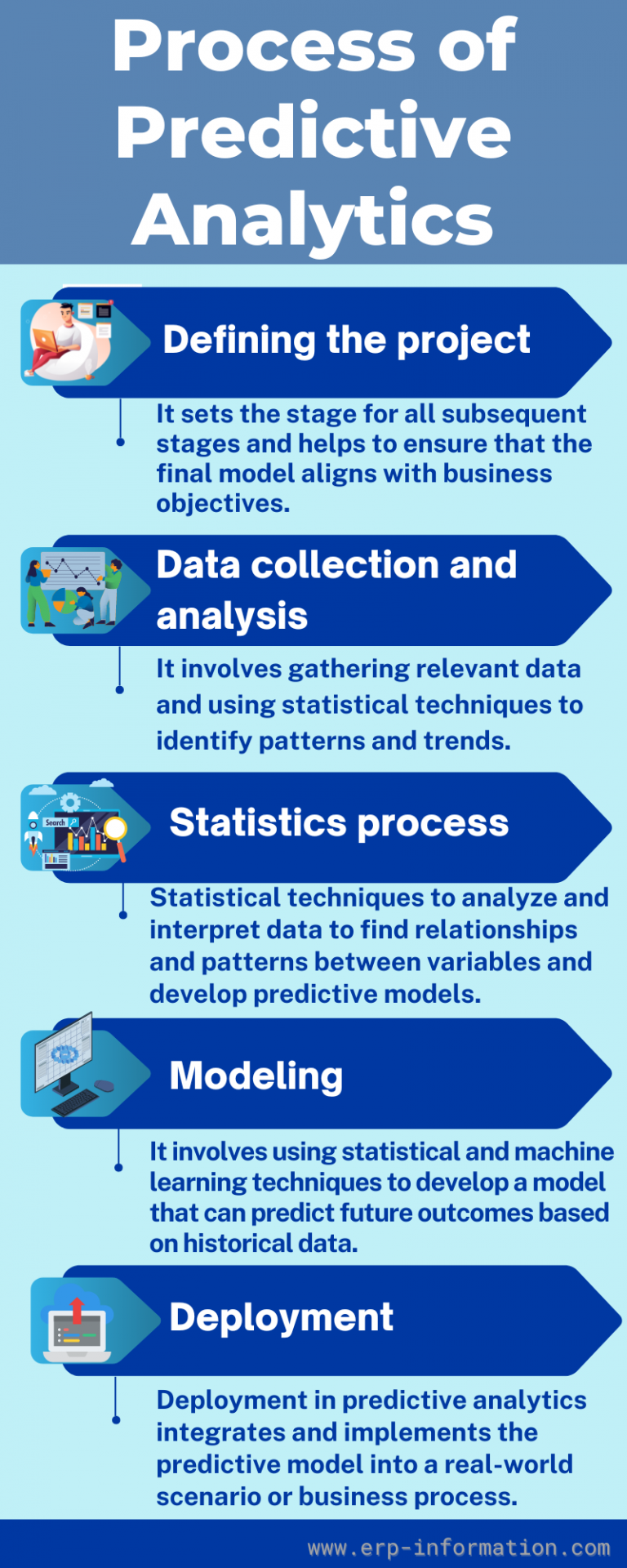
Building and Validating PA Models
The process of building and validating PA models involves several key steps. First, researchers must select the most influential variables affecting the response. This is followed by splitting the dataset into training and validation sets. The training set is used to build the model, while the validation set assesses its performance. This helps in identifying and mitigating issues like overfitting, where a model performs well on training data but poorly on new data.
Challenges in Predictive Analytics
Despite its benefits, predictive analytics faces several challenges. One major issue is overfitting, which occurs when a model learns the noise in the training data rather than the underlying patterns. Another challenge is the bias-variance trade-off, where reducing bias increases variance and vice versa. Balancing these factors is crucial for creating models that generalize well to new data.
Evaluating Model Accuracy
Zahavi emphasizes the importance of evaluating model accuracy using various metrics. These include accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score. Additionally, he highlights the need to compare the goodness-of-fit between training and validation datasets. A model that performs similarly on both datasets is considered a good candidate.
Applications Across Industries
Predictive analytics is applied across a wide range of industries, each with its unique challenges and requirements.
Industrial Applications
In the industrial sector, PA is used to optimize processes, improve supply chain management, and enhance equipment maintenance. For example, big data analytics helps in predicting equipment failures, allowing for proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
E-commerce Applications
E-commerce platforms leverage PA to understand customer behavior, personalize recommendations, and optimize inventory management. Machine learning algorithms analyze vast amounts of data to predict trends and improve customer satisfaction.
Smart Healthcare Applications
In healthcare, PA is used to predict patient outcomes, manage chronic diseases, and improve treatment plans. Predictive models can identify patients at risk of certain conditions, enabling early intervention and better resource allocation.
Smart Agriculture Applications
Agriculture benefits from PA through crop yield predictions, soil health monitoring, and weather forecasting. These insights help farmers make informed decisions, leading to increased productivity and sustainability.
Smart City Applications
Smart cities use PA to manage traffic flow, reduce energy consumption, and enhance public safety. By analyzing real-time data, city planners can make data-driven decisions to improve urban living.
ICT Applications
In the information and communication technology (ICT) sector, PA is used to optimize network performance, detect anomalies, and improve cybersecurity. Predictive models help in identifying potential threats and ensuring system reliability.
Weather Applications
Weather prediction is another critical area where PA plays a significant role. Accurate forecasts help in disaster preparedness, agricultural planning, and resource management. Advanced models analyze historical weather data to predict future conditions with greater accuracy.
Future Trends and Innovations
As technology continues to evolve, the future of predictive analytics looks promising. Emerging technologies like deep learning and natural language processing (NLP) are expected to enhance the capabilities of PA models. These technologies can handle unstructured data, making predictions more accurate and comprehensive.
The Impact of Deep Learning
Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, has shown remarkable success in various domains. Its ability to learn from large datasets makes it ideal for complex predictive tasks. For instance, deep learning models can analyze social media data to predict consumer trends, providing valuable insights for businesses.
Enhancing Business Efficiency
By leveraging predictive analytics, businesses can gain a competitive edge. Accurate predictions allow companies to make informed decisions, reduce costs, and improve customer experiences. Whether it’s optimizing supply chains, personalizing marketing strategies, or enhancing product development, PA offers numerous benefits.
In conclusion, predictive analytics is a powerful tool that transforms raw data into actionable insights. As organizations continue to embrace big data, the role of PA will only grow. With ongoing advancements in technology and methodologies, the future of predictive analytics holds immense potential for innovation and growth.