The Power of an International Portfolio: Diversification, Risks, and Opportunities
An international portfolio is a strategic investment approach that allows investors to gain exposure to foreign markets, offering both opportunities and challenges. This type of portfolio includes stocks, bonds, and other assets from emerging and developed economies, enabling investors to diversify their holdings beyond domestic markets. As global financial markets become increasingly interconnected, understanding the benefits and risks of an international portfolio is essential for any investor looking to build a well-rounded investment strategy.
What Is an International Portfolio?
An international portfolio is a collection of investments focused on foreign assets rather than domestic ones. It provides investors with access to a broader range of economic environments, including both developed and emerging markets. By spreading investments across different countries, investors can reduce the risk associated with overexposure to a single economy.
This strategy can be particularly appealing to those seeking growth in fast-growing economies such as China or India. However, it also comes with unique risks, such as currency fluctuations, political instability, and varying regulatory frameworks. Despite these challenges, an international portfolio can offer significant advantages when managed effectively.
Key Takeaways
- An international portfolio offers exposure to global markets, including both developed and emerging economies.
- Diversification is one of the primary benefits, helping to reduce risk by spreading investments across different regions.
- Currency exchange rate risk and political/economic instability are key concerns for international investors.
- Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are a cost-effective way to gain exposure to international markets.
Understanding the International Portfolio
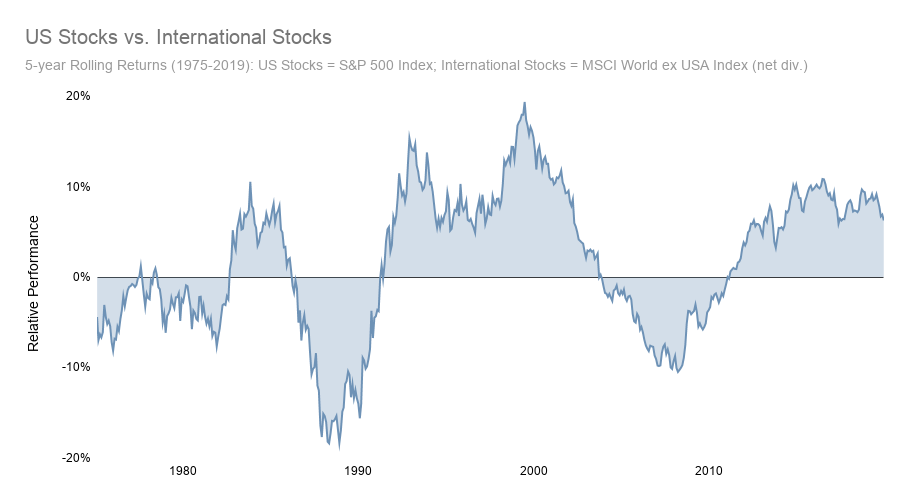
Investors often turn to international portfolios to mitigate the risks associated with relying solely on domestic markets. While the U.S. market has historically been a strong performer, it is not immune to downturns. An international portfolio can help smooth out returns by balancing performance across different regions.
For example, if U.S. stocks decline, gains in international holdings may offset some of the losses. This balance can be further enhanced by including a mix of stocks from both developed and emerging markets. Developed markets like Europe and Japan tend to be more stable, while emerging markets such as India and Brazil offer higher growth potential but come with greater volatility.
Another factor to consider is currency exposure. When investing internationally, you are effectively buying the currencies in which the assets are quoted. This means that changes in exchange rates can impact the value of your portfolio. For instance, if the U.S. dollar weakens against the British pound, your investment in a London-listed stock could increase in value.
Risks and Rewards of International Investing

While international portfolios can offer substantial rewards, they also come with unique risks. Political and economic instability in some countries can lead to sharp declines in stock prices. For example, a sudden change in government policy or a financial crisis in a developing nation can significantly impact an investor’s returns.
Additionally, transaction costs can be higher when investing in foreign markets. Brokers often charge more for international trades, and there may be additional fees related to currency conversion, taxes, and regulatory requirements. These costs can eat into profits, making it important for investors to carefully evaluate their options.
Currency exchange rate risk is another critical factor. Fluctuations in exchange rates can either enhance or diminish the value of international investments. If the local currency of a foreign market depreciates relative to the U.S. dollar, the value of your investment could decrease even if the underlying assets perform well.
Advantages of an International Portfolio
Despite the risks, an international portfolio offers several compelling advantages:
1. Risk Reduction
By diversifying across multiple markets, investors can reduce the overall risk of their portfolio. If one region underperforms, gains in another may help offset the losses. This is especially useful during periods of economic uncertainty or market volatility.
2. Diversified Currency Exposure
Investing in foreign markets exposes investors to different currencies, which can act as a hedge against fluctuations in the U.S. dollar. This helps to stabilize returns and reduce the impact of currency movements on the portfolio.
3. Market Cycle Timing
Different countries experience economic cycles at different times. By holding an international portfolio, investors can take advantage of these variations. For example, if the U.S. market is overvalued, an investor might look for opportunities in emerging markets that are undervalued and poised for growth.
4. Access to Growth Opportunities
Emerging markets often offer faster growth than developed economies. By including these markets in a portfolio, investors can benefit from the expansion of companies in countries like China, India, and Brazil.
Disadvantages of an International Portfolio
While the benefits are clear, there are also several disadvantages to consider:
1. Political and Economic Risk
Many developing countries face political and economic instability, which can lead to unpredictable market behavior. A sudden change in government policy or a financial crisis can cause significant losses for investors.
2. Increased Transaction Costs
As mentioned earlier, investing internationally often involves higher transaction costs. These include brokerage fees, currency conversion charges, and other administrative expenses that can reduce overall returns.
3. Currency Exchange Rate Risk
Fluctuating exchange rates can impact the value of international investments. A drop in the value of a foreign currency relative to the U.S. dollar can result in losses, even if the underlying assets perform well.
How to Build an International Portfolio
For most retail investors, building an international portfolio requires careful planning and professional guidance. Here are some steps to consider:
- Consult a Financial Advisor: A professional can help determine the right allocation based on your investment goals and risk tolerance.
- Use ETFs or Mutual Funds: These vehicles provide broad exposure to international markets at a lower cost compared to individual stock purchases.
- Monitor Currency Trends: Keep an eye on exchange rates and consider hedging strategies if necessary.
- Diversify Across Regions: Spread investments across different continents and economies to minimize risk.
Conclusion
An international portfolio is a powerful tool for investors seeking to diversify their holdings and tap into global growth opportunities. While it comes with its share of risks, the potential rewards make it a valuable addition to any investment strategy. By understanding the dynamics of international markets and managing risks effectively, investors can create a balanced portfolio that withstands economic fluctuations and capitalizes on global trends. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, considering an international portfolio could be a smart move toward long-term financial success.


